Goods & Service Tax(GST)
Goods and Services Tax (GST) is an indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services. GST is a destination-based tax that replaces earlier central taxes and duties such as excise duty, service tax, countervailing duty (CVD), special additional duty of customs (SAD), central charges, and local state taxes such as value-added tax (VAT), central sales tax (CST), entry tax, purchase tax, luxury tax, state cesses and surcharges, and entertainment tax. The foremost objective of GST is
- To create a common market in India with a uniform taxation system.
- To eliminate the cascading effect of taxes.
- To reduce the need for multiple documentation under the previous taxation system.
- To simplify the entire process of paying taxes.
- To increase the taxpayer base.
Records to be maintained Under GST
Each registered person is required to maintain correct records of the following:
- Production or manufacture of goods
- Inward and outward supply of goods or services, or both
- Stock of goods
- Input tax credit availed
- Output tax payable and paid
- Any other particulars deemed necessary
The above records must be maintained at each place of business registered under GST.
Accounts to be maintained Under GST
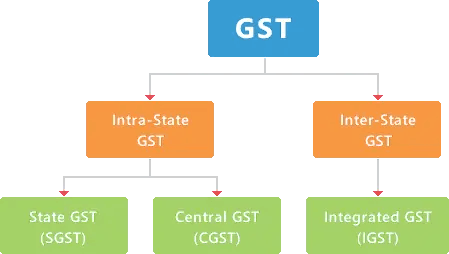
Intra-state GST : When supply is made within the state, it is termed intra-state. On intra-state transactions, State GST (SGST) and Central GST (CGST) are levied at half the prescribed rate.
Inter-State GST : When supply is made outside the state, it is termed inter-state. On inter-state transactions, Integrated GST (IGST) is levied at the full prescribed rate.
I. Input GST
- Input GST is the GST paid by the purchaser of Goods/Service.
- Input GST is treated as an Asset in the books of Purchaser.
II. Output GST
- Output GST is the GST collected by the seller of Goods/Service.
- Output GST is treated as a Liability in the books of the seller.
Wherever ITC is allowed, the input GST can be set off against Output GST. If there is any balance in the Output GST, then it is to be paid to the Government.
III. Reverse Charge
When GST is directly paid by the purchaser of Goods/Services to the Government, it is known as Reverse Charge. It may be done for
- Fee paid to a lawyer.
- Fee paid outside India.
- Payment for Copyright.
- For Goods/Services purchased from unregistered taxpayer.
The following accounts should be maintained by the registered person
- Input CGST
- Input SGST
- Output CGST
- Output SGST
- Input IGST
- Output IGST
Maintaining Electronic Cash Ledger
Electronic Cash Ledger is an account of the taxpayer maintained by GST system. The Electronic Cash Ledger contains a summary of all the deposits/payments made by a taxpayer. The Cash deposits can be used for making payment(s) like tax liability, interest, penalties, fee, and others.
Let us understand with some examples. You have a trading concern ‘Shiva Auto Spares’ in Chandigarh.
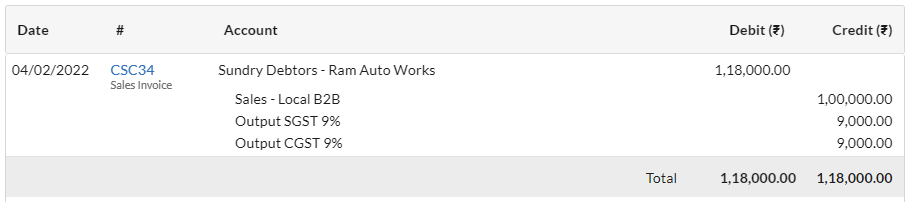
- You have bought goods from Danial Bearings in Chandigarh for Rs.25,000 applicable rate of GST 18%.
- You sold goods to Ram Auto Works in Chandigarh for Rs.20,000 applicable rate of GST 18%.
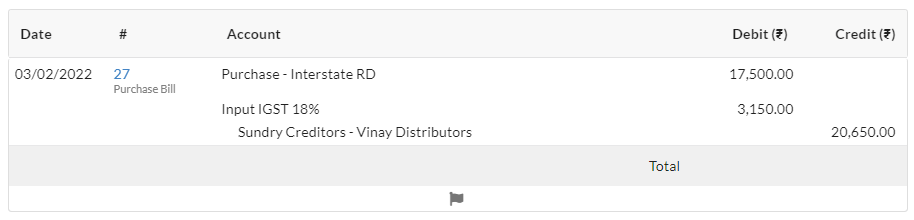
- You have bought goods from Arunachal Pradesh for Rs.17,500 applicable rate of GST 18%.
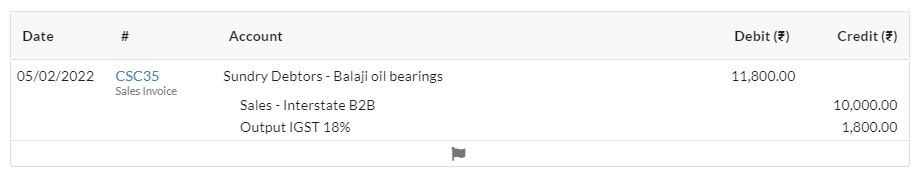
- You sold goods to Balaji oil bearings located in Tamil Nadu for Rs.10,000 applicable rate of GST 18%.
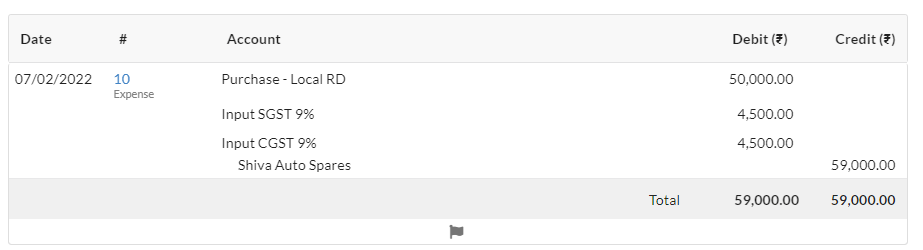
- You have purchased Computer for Office use within the state for Rs.50,000.
1. Purchase Transaction (Intra-State – Inward Supplies of Goods/Services)
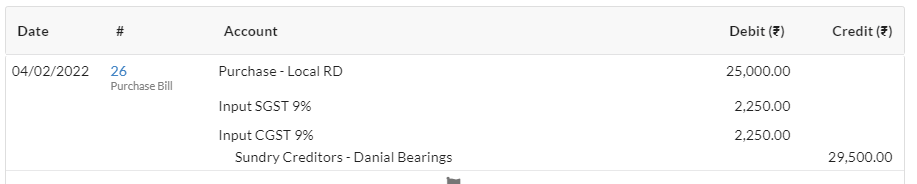
2. Sales Transaction (Intra-State – Outward Supplies of Goods/Services)
3. Purchase Transaction (Inter-State – Inward Supplies of Goods/Services)
4. Sales Transaction (Inter-State – Outward Supplies of Goods/Services)
5. Purchase Transaction (Intra-State – Inward Supplies of Goods/Services)
By these entries, we get
Total Input CGST = 2,250 + 4,500 = 6750
Total Output CGST = 9000
Net CGST Payable = Output CGST – Input CGST = 9000 – 6750 = 2250
Total Input SGST = 2,250 + 4,500 = 6750
Total Output SGST = 9000
Net SGST Payable = Output SGST – Input SGST = 9000 – 6750 = 2250
Total Input IGST = 3150
Total Output IGST = 1800
1) IGST Credit is set off against the IGST liability = 3150 – 1800 = 1350.
2) IGST credit Rs.1350 is available.
3) This will be first applied to the Net CGST liability. 2250 – 1350 = 900.
4) So, the output tax payable is the remaining CGST liability plus the net SGST liability.
Output tax payable = 900 + 2250 = 3150
The protocol for availing and utilizing the credit of these taxes is as follows:
| Credit of | To be utilized first for the payment of | May be further utilized for the payment of | |
|---|---|---|---|
| CGST | CGST | IGST | |
| SGST | SGST | IGST | |
| IGST | IGST | CGST, then SGST |
| Particulars | CGST | SGST | IGST |
|---|---|---|---|
| Output Liability | 9000 | 9000 | 1800 |
| Less : Input Tax Credit | |||
| IGST | 1350 | – | 1800 |
| CGST | 6750 | – | – |
| SGST | – | 6750 | – |
| Amount Payable | 900 | 2250 | – |
Adjustment Entries
The Set-Off entries will be as follows
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Set Off against CGST Output | ||
| Output CGST 9% | 8100 | |
| To Input CGST 9% | 6750 | |
| To Input IGST 18% | 1350 | |
| Set Off against SGST Output | ||
| Output SGST 9% | 6750 | |
| To Input SGST 9% | 6750 | |
| Set Off against IGST Output | ||
| Output IGST 18% | 1800 | |
| To Input IGST 18% | 1800 | |
| Final Payment | ||
| Output CGST 9% | 900 | |
| Output SGST 9% | 2250 | |
| To Electronic Cash Ledger | 3150 |
Retention Period of records under GST
Every person registered under GST must retain and maintain records and accounts for a minimum of 72 months from the date of filing their annual return. At the end of the year, you can reconcile your purchase register with the invoices uploaded by your suppliers on the GST government portal using our GSTR-2 reconciliation report.